First Modern Olympic Games, Greece 1896

On April 6, 120 years ago, the Olympic Games, its spirit, and modern ideals, were reborn in Athens, Greece. They were not the first attempt, nor born overnight, and came some 1600 years after the last ancient Greek games which had run for nearly 1200 years every 4th year or olympiad. In 394 AD the Roman Christian emperor Theodosius banned all pagan festivals including the Olympics, despite New Testament metaphors drawing inspiration from athletics. It took a Frenchman, inspired by the traditions of several English towns and cities, in combination with the philanthropy of two Greek brothers – who rebuilt an all-marble sports facility on the site of an ancient Athenian stadium, to restore the Olympic Games that we know today.
History of pre-Modern Olympics Games
Several attempts to bring back the Olympic Games were made during the nineteenth century and earlier. Some were local and just used the Olympic name. These included the Cotswold Olimpick Games, near Chipping Campden in England, first organised by Robert Dover between 1612 and 1642.
220 years ago, revolutionary France launched L’Olympiade de la République, between 1796 and 1798 in front of 300,000 spectators in Paris. These games included a chariot race and were dedicated to la paix et à la fécondité – “peace and fertility”. The 1798 Games introduced metric distances and measurements for the first time.

In 1850 Dr William Penny Brookes founded an Olympic event at Much Wenlock, Shropshire, which, in 1859, became known as the Wenlock Olympian Games. Still continuing to this day, its aim was:
“to promote the moral, physical and intellectual improvement of the inhabitants of the town and neighbourhood of Wenlock, and especially of the working classes, by the encouragement of outdoor recreation and by the award of a prize…”
Not to be left out, Liverpool held an annual Grand Olympic Festival between 1862 and 1867, including events in Llandudno 1965-1966. They were founded by John Hulley and Charles Melly, and were open to all local and international ‘gentlemen amateurs’, although the first truly national Olympic Games were held at Crystal Palace Park Cricket Ground and on the River Thames at Teddington, 31 July 1866. In 1869, Hulley also organised Britain’s first velocipede and bicycle races, at which the UK now excels.
Leicester, in 1866, also held a Grand Olympic Festival, on the site of the current University of Leicester, Fielding Johnson Building, but which was formerly the Leicestershire and Rutland Lunatic Asylum.
The forerunner to the British Olympic Association was the Liverpool-founded National Olympian Association, in 1865, which went on to inspire the International Olympic Charter. The OC outlines the “fundamental principles of Olympism” and rules of the International Olympic Committee (IOC).
Olympic Games, Athens
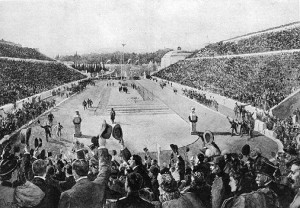
The 1820s and 30s had seen interest in a revival of the Olympic Games gathering momentum. In 1856 the sponsorship of Evangelos and Konstantinos Zappas was accepted by the Greek king to fund the restoration of the Panathenaiko Stadio, or “Panathenaic Stadium“, in Athens. This was not, in fact, the original ancient Games location, since the older panhellenic Games were held at Olympia, but instead, part of the Athenian Games tradition. 1859, 1870 and 1875, then saw the first modern Greek Olympics held.
In 1890, Frenchman Baron Pierre de Coubertin, was inspired to found the International Olympic Committee after visiting the Wenlock Olympian Games. This led to the first international Games, of 1896, also at Athens. The top prize was actually a Silver Medal, rather than Gold.

There were just 9 sports and 43 events over 10 days, but, significantly, the marathon, actually run from Marathon, was won by Greek athlete Spyridon “Spyro” Louis in front of 100,000 spectators.
Women’s Olympic Games
Although Athens, was not dissimilar to the Games of Liverpool and Wenlock, it was still unlike our truly modern Games, in that women were excluded from their late-nineteenth century revivals.
De Coubertin was opposed to women competing, although in 1900 they were allowed to enter tennis and gold, and London in 1908 added the Figure Skating event for women, gradually women became involved. This was not fast enough for another French national, and rower, Alice Milliat, who founded the independent Women’s Olympics in Paris in 1922, continuing through to 1934, owing to the refusal of the IOC to allow women to enter track and field events. The IOC forced a name change in 1928 to the Women’s World Games, in exchange for grudgingly admitting more events for women at the Olympics.
Even in ancient Olympics, although separate, there were some female Games, such as those of Hera at Olympia which included a separate racing competition for women. Spartan women used to take part in sports and exercises, semi-clothed – with one breast exposed, like Amazon archers, leading to a “remarkable conjunction of homosexuality, feminism, and athletics” at Sparta. Plutarch suggests that younger Spartan girls and boys would compete and exercise in the nude alongside each other.
Ancient Olympic Traditions
Most of the ancient Olympics were competed in, naked – and only by Greek-speaking freemen. For a while, women were able to enter chariot horse teams, but not enter themselves. Furthermore, they could not spectate if they were married women. Stories tell of one chariot team owner being caught crossdressing as a man to enter the trainers area and watch her team which led to even trainers having to be in the nude. Even the word ‘gymnasium’, comes from the Greek gymnos, “naked”.
“The modern Olympic ideal is completely alien to the spirit of the Greek original, which despised women, slaves and foreigners and celebrated sectarian religion, nudity, pain and winning at any cost.” – Christopher Howse, Daily Telegraph, Athens 2004
Early-on, loincloths were outlawed among the competitors and the only thing allowed was a kunodesme, “putting the dog on the lead”, penis-strap, to stop it getting in the way. Many events involved the athletes covering themselves in olive oil – the mind boggles at the wrestling events!
“The attempt to link modern athletes and ancient athletes inevitably runs up against major cultural differences…we must never lose sight of the popular savagery of the pankration. Even in more conventional events, antiquity showed a tolerance, or perhaps a taste, that is utterly alien to the modern world.” – New Republic, 2004
Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2016
The ancient Games included sacrifices to the gods, the effective wearing of knuckle-dusters in the boxing, and opportunities for music and the arts alongside the body-worship and savagery. The next Games in Rio, this summer, may omit the sacrifices and savagery, and the nudity, but will still put athletic bodies centre-stage. The modern Olympic ideal of the taking part being more important than the winning, is long gone. Instead, we have doping and bribery scandals, not to mention long-running issues over the place of intersex athletes and how to include and ‘define’ them, given that the Games now includes women in most of its events rather than the original’s men-only events. The IOC can’t make up its mind on the definition of male and female athletes (like Caster Semenya and Dutee Chand), leaving many intersex athletes out in the cold, censured, or even facing compulsory surgeries to conform to standardised sex ideals.
The mission of Olympic Spirit is to:
“build a peaceful and better world in the Olympic Spirit which requires mutual understanding with a spirit of friendship, solidarity and fair play – Olympic Spirit strives to inspire and motivate the youth of the world to be the best they can be through educational and entertaining interactive challenges. Olympic Spirit seeks to instill and develop the values and ideals of Olympism in those who visit and to promote tolerance and understanding in these increasingly troubled times in which we live, to make our world a more peaceful place.”